原题:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3379
【模板】最近公共祖先(LCA)
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入格式
第一行包含三个正整数 ,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来 行每行包含两个正整数 ,表示 结点和 结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来 行每行包含两个正整数 ,表示询问 结点和 结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式
输出包含 行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| 5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5
|
样例输出 #1
提示
对于 的数据,,。
对于 的数据,,。
对于 的数据,,,不保证 。
样例说明:
该树结构如下:
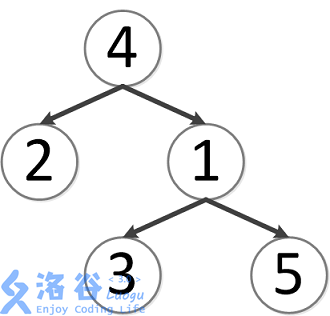
第一次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第二次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第三次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第四次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第五次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
故输出依次为 。
倍增法是一种用于在树中快速找到两个节点的最近公共祖先(LCA)的算法。它的核心思想是通过预处理和二进制跳跃来高效地找到公共祖先。
看了里面的题解,大概分为三步
深度优先搜索,获得每个结点的深度和祖先

dfs找深度和祖先
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void dfs(int me,int fa) {
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[depth[me]]; ++i)
father[me][i] = father[father[me][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int son : g[me])
if (son!=fa)
{
depth[son] = depth[me] + 1;
father[son][0] = me;
dfs(son,me);
}
}
|
father[x][i] 表示节点 x 向上跳 2^i 步后的祖先节点。lg[depth[x]] 表示节点 x 的深度的对数值,用于确定最大跳跃步数。对数表可以提前生成好
1
2
3
4
| void init_lg() {
for (int i = 2; i < N; ++i)
lg[i] = lg[i>>1] + 1;
}
|
表格如下:
| x |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
… |
| lg[x] |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
… |
寻找公共祖先,先将更深的点回溯到与另一个点深度相同的位置

快速回溯到深度相同
1
2
3
4
5
| if (depth[x] < depth[y])
swap(x, y);
while(depth[x]>depth[y])
x=father[x][lg[depth[x]-depth[y]]];
if (x == y) return x;
|
逐跳往上找公共祖先

逐跳往上找公共祖先
1
2
3
4
| for (int i = lg[depth[x]]; i >= 0; --i)
if (father[x][i] != father[y][i])
x = father[x][i],y = father[y][i];
return father[x][0];
|
- 从最大的
i 开始(即从最大的跳跃步数开始),逐步减少 i,检查节点 x 和 y 的 2^i 祖先是否相同。
- 如果
father[x][i] 和 father[y][i] 不相同,则将 x 和 y 更新为它们的 2^i 祖先。
- 目的:将
x 和 y 同时向上移动,直到它们的祖先相同。
- 当循环结束时,
x 和 y 的最近公共祖先就是 father[x][0],即 x 和 y 的直接父节点。
总代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 500005;
int n, q, root;
vector<int> g[N];
int lg[N];
int father[N][31];
int depth[N];
void init_lg() {
for (int i = 2; i < N; ++i)
lg[i] = lg[i>>1] + 1;
}
void dfs(int me,int fa) {
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[depth[me]]; ++i)
father[me][i] = father[father[me][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int son : g[me])
if (son!=fa)
{
depth[son] = depth[me] + 1;
father[son][0] = me;
dfs(son,me);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (depth[x] < depth[y])
swap(x, y);
while(depth[x]>depth[y])
x=father[x][lg[depth[x]-depth[y]]];
if (x == y) return x;
for (int i = lg[depth[x]]; i >= 0; --i)
if (father[x][i] != father[y][i])
x = father[x][i],y = father[y][i];
return father[x][0];
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &q, &root);
init_lg();
int x, y;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(root,root);
while (q--) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", lca(x, y));
}
return 0;
}
|



